Spark的流式数据处理
Spark的流式数据处理
流式数据处理,有好多种形态,本文介绍最简单的一种场景:用户输入一行数据,Spark负责统计这行数据里面的各个words的个数。
Spark自己提供了代码1,在这里:
完整的代码贴在下面:
/*
* Licensed to the Apache Software Foundation (ASF) under one or more
* contributor license agreements. See the NOTICE file distributed with
* this work for additional information regarding copyright ownership.
* The ASF licenses this file to You under the Apache License, Version 2.0
* (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
* the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
*
* http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
*
* Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
* distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
* WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
* See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
* limitations under the License.
*/
// scalastyle:off println
package org.apache.spark.examples.streaming
import org.apache.spark.SparkConf
import org.apache.spark.storage.StorageLevel
import org.apache.spark.streaming.{Seconds, StreamingContext}
/**
* Counts words in UTF8 encoded, '\n' delimited text received from the network every second.
*
* Usage: NetworkWordCount <hostname> <port>
* <hostname> and <port> describe the TCP server that Spark Streaming would connect to receive data.
*
* To run this on your local machine, you need to first run a Netcat server
* `$ nc -lk 9999`
* and then run the example
* `$ bin/run-example org.apache.spark.examples.streaming.NetworkWordCount localhost 9999`
*/
object NetworkWordCount {
def main(args: Array[String]) {
if (args.length < 2) {
System.err.println("Usage: NetworkWordCount <hostname> <port>")
System.exit(1)
}
StreamingExamples.setStreamingLogLevels()
// Create the context with a 1 second batch size
val sparkConf = new SparkConf().setAppName("NetworkWordCount")
val ssc = new StreamingContext(sparkConf, Seconds(1))
// Create a socket stream on target ip:port and count the
// words in input stream of \n delimited text (eg. generated by 'nc')
// Note that no duplication in storage level only for running locally.
// Replication necessary in distributed scenario for fault tolerance.
val lines = ssc.socketTextStream(args(0), args(1).toInt, StorageLevel.MEMORY_AND_DISK_SER)
val words = lines.flatMap(_.split(" "))
val wordCounts = words.map(x => (x, 1)).reduceByKey(_ + _)
wordCounts.print()
ssc.start()
ssc.awaitTermination()
}
}
// scalastyle:on println
关于这个代码的讲解,可以看Spark提供的文档2。简单来讲,这个代码就是每秒钟执行一次,等待从9999端口发来的一行一行数据,然后统计每行数据的words的个数。
在启动这个数据处理代码之前,先把客户端跑起来:
$ nc -lk 9999
如上所示,使用nc这个网络工具,打开9999端口,并等待用户从终端输入数据。
此时我们启动NetworkWordCount这个数据处理代码:
$ run-example streaming.NetworkWordCount localhost 9999
它会在终端里保持运行,每隔一秒钟读取9999端口的数据。运行状态如下:
此时在客户端输入一些数据:
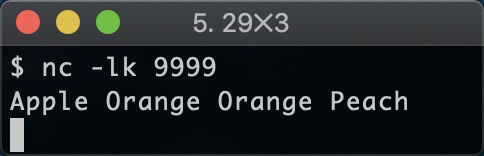
可以看到数据处理端的输出结果:
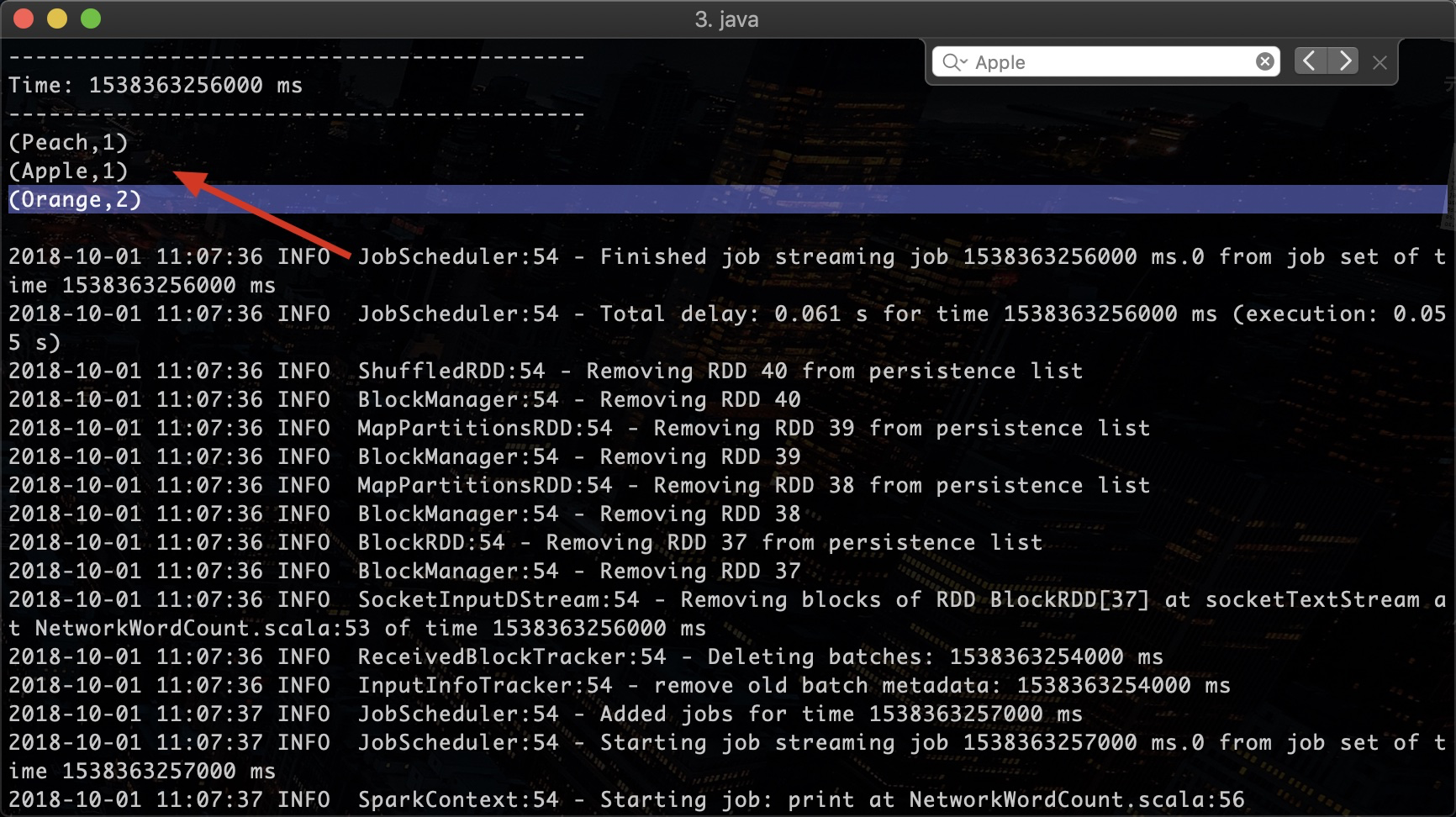
以上是Spark的Stream处理的一个最简单的场景。更复杂的流式数据处理场景,可以查看Spark的文档3,学习各种模式。