RESTEasy的decorator机制
本文分析RESTEasy针对JAXB的Decorator扩展功能。主要的任务是撰写Decorator和DecoratorProcessor。下面是例子:
package io.weli;
import org.jboss.resteasy.annotations.Decorator;
import javax.xml.bind.Marshaller;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
@Target({ElementType.TYPE, ElementType.METHOD, ElementType.PARAMETER, ElementType.FIELD})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Decorator(processor = FooMarshallerDecoratorProcessor.class, target = Marshaller.class)
public @interface FooMarshallerDecorator {
}
上面的Decorator会用来标记rest方法,后续会用到。然后这个Decorator会使用对应的processor:
package io.weli;
import org.jboss.resteasy.annotations.DecorateTypes;
import org.jboss.resteasy.spi.DecoratorProcessor;
import javax.ws.rs.core.MediaType;
import javax.xml.bind.Marshaller;
import java.lang.annotation.Annotation;
@DecorateTypes({"text/*+xml", "application/*+xml"})
public class FooMarshallerDecoratorProcessor implements DecoratorProcessor<Marshaller, FooMarshallerDecorator>
{
public Marshaller decorate(Marshaller target, FooMarshallerDecorator annotation,
Class type, Annotation[] annotations, MediaType mediaType)
{
System.out.println("FooMarshallerDecoratorProcessor for Marshaller");
return target;
}
}
比如上面的FooMarshallerDecorator里,使用的processor是FooMarshallerDecoratorProcessor。然后就可以写一个resource来验证:
import javax.ws.rs.Consumes;
import javax.ws.rs.POST;
import javax.ws.rs.Path;
import javax.ws.rs.Produces;
import javax.ws.rs.core.MediaType;
import javax.ws.rs.core.Response;
@Path("/order")
public interface OrderResource {
@POST
@Path("/update")
@Consumes({MediaType.APPLICATION_XML, MediaType.TEXT_XML})
@Produces(MediaType.APPLICATION_XML)
@FooMarshallerDecorator
Response update(FooJaxbEntity obj);
}
上面这个OrderResource里,使用了FooMarshallerDecorator这个标记。这样,这个decorator对应的processor就会被执行。可以撰写测试代码:
package io.weli;
import org.jboss.resteasy.plugins.server.undertow.UndertowJaxrsServer;
import org.jboss.resteasy.test.TestPortProvider;
import org.junit.AfterClass;
import org.junit.BeforeClass;
import org.junit.Test;
import javax.ws.rs.ApplicationPath;
import javax.ws.rs.client.Client;
import javax.ws.rs.client.ClientBuilder;
import javax.ws.rs.client.Entity;
import javax.ws.rs.core.Application;
import javax.ws.rs.core.Response;
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.Set;
public class TestTest {
private static UndertowJaxrsServer server;
@BeforeClass
public static void init() throws Exception {
server = new UndertowJaxrsServer().start();
}
@AfterClass
public static void stop() throws Exception {
server.stop();
}
@Test
public void testApplicationPath() throws Exception {
server.deploy(TestApp.class);
Client client = ClientBuilder.newClient();
Response resp = client
.target(TestPortProvider.generateURL("/base/order/update"))
.request()
.post(Entity.xml(new FooJaxbEntity("test_test")));
System.out.println("entity: " + resp.getEntity());
client.close();
}
@ApplicationPath("/base")
public static class TestApp extends Application {
@Override
public Set<Class<?>> getClasses() {
HashSet<Class<?>> classes = new HashSet<>();
classes.add(OrderResourceImpl.class);
return classes;
}
}
}
然后执行看到结果:
in order resource impl
FooMarshallerDecoratorProcessor for Marshaller
entity: org.jboss.resteasy.client.jaxrs.internal.ClientResponse$InputStreamWrapper@6d2260db
可以看到processor被执行了。这个执行的逻辑是放在AbstractJAXBProvider里面:
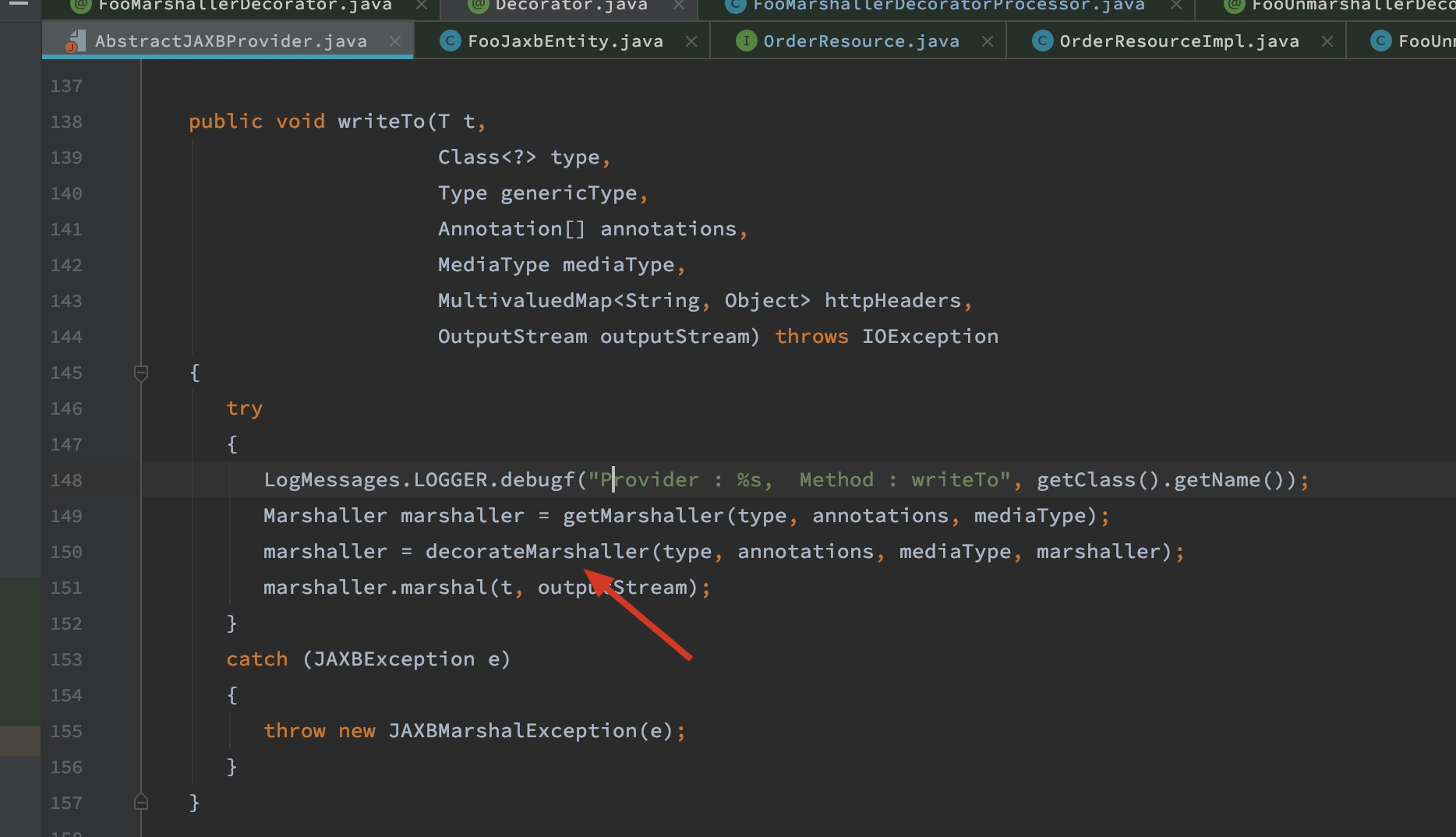
可以看到这个decoratorMarshaller(...)方法在做decorator的处理工作。进到decorateMarshaller方法内部看一看具体的实现:
public static Marshaller decorateMarshaller(Class type, Annotation[] annotations, MediaType mediaType, Marshaller marshaller) throws JAXBException
{
DecoratorMatcher processor = new DecoratorMatcher();
return processor.decorate(Marshaller.class, marshaller, type, annotations, mediaType);
}
可以看到是DecoratorMatcher的decorate方法在做具体的工作。以下是这个方法的具体实现:
/**
* @param targetClass i.e. Marshaller
* @param target target object
* @param type i.e. a JAXB annotated class
* @param annotations i.e. method or parameter annotations
* @param mediaType media type
* @param <T> type
* @return decorated target object
*/
@SuppressWarnings(value = "unchecked")
public <T> T decorate(Class<T> targetClass, T target, Class type, Annotation[] annotations, MediaType mediaType)
{
HashMap<Class<?>, Annotation> meta = new HashMap<Class<?>, Annotation>();
if (type != null)
{
registerDecorators(targetClass, meta, type.getAnnotations());
}
// override any class level ones
if (annotations != null)
{
registerDecorators(targetClass, meta, annotations);
}
if (meta.size() == 0) return target;
MediaTypeMap<Class<?>> typeMap = new MediaTypeMap<Class<?>>();
for (Class<?> decoratorAnnotation : meta.keySet())
{
Decorator decorator = decoratorAnnotation.getAnnotation(Decorator.class);
String[] mediaTypes = {"*/*"};
DecorateTypes produces = decorator.processor().getAnnotation(DecorateTypes.class);
if (produces != null)
{
mediaTypes = produces.value();
}
for (String pType : mediaTypes)
{
typeMap.add(MediaType.valueOf(pType), decoratorAnnotation);
}
}
List<Class<?>> list = typeMap.getPossible(mediaType);
for (Class<?> decoratorAnnotation : list)
{
Annotation annotation = meta.get(decoratorAnnotation);
Decorator decorator = decoratorAnnotation.getAnnotation(Decorator.class);
DecoratorProcessor processor = null;
try
{
processor = decorator.processor().newInstance();
}
catch (InstantiationException e)
{
throw new RuntimeException(e.getCause());
}
catch (IllegalAccessException e)
{
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
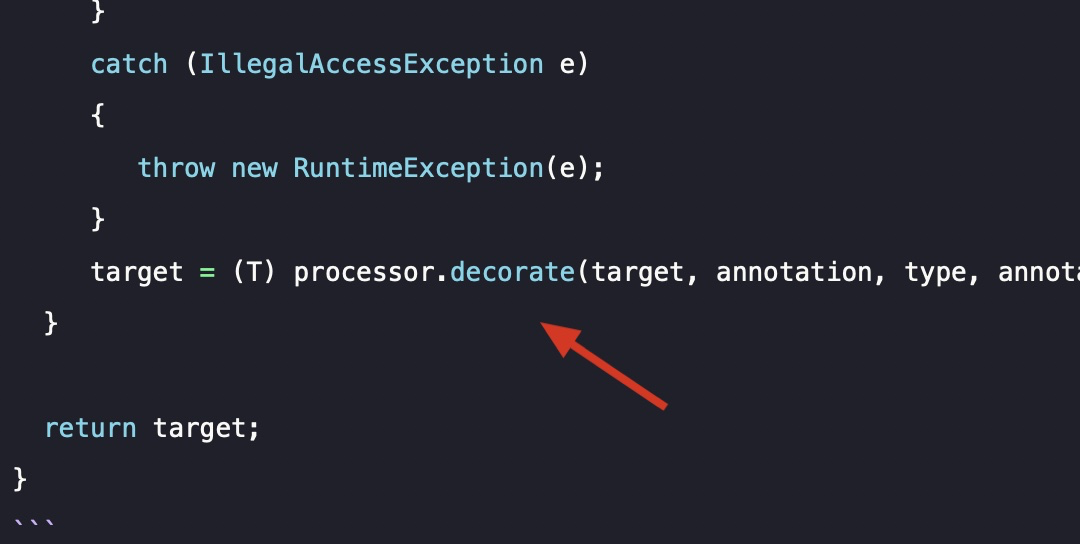
target = (T) processor.decorate(target, annotation, type, annotations, mediaType);
}
return target;
}
可以看到上面的处理代码当中对Decorator,DecoratorTypes,DecoratorProcessor的使用。这个方法是一个通用的,所以需要之前看到的:
@Decorator(processor = FooMarshallerDecoratorProcessor.class, target = Marshaller.class)
public @interface FooMarshallerDecorator {
...
}
以及:
@DecorateTypes({"text/*+xml", "application/*+xml"})
public class FooMarshallerDecoratorProcessor implements DecoratorProcessor<Marshaller, FooMarshallerDecorator>
...
这里面传入的target = Marshaller,和processor = FooMarshallerDecoratorProcessor.class,在上面的decorate方法当中都做了匹配,然后根据匹配到的具体class,执行对应processor的decorate方法:
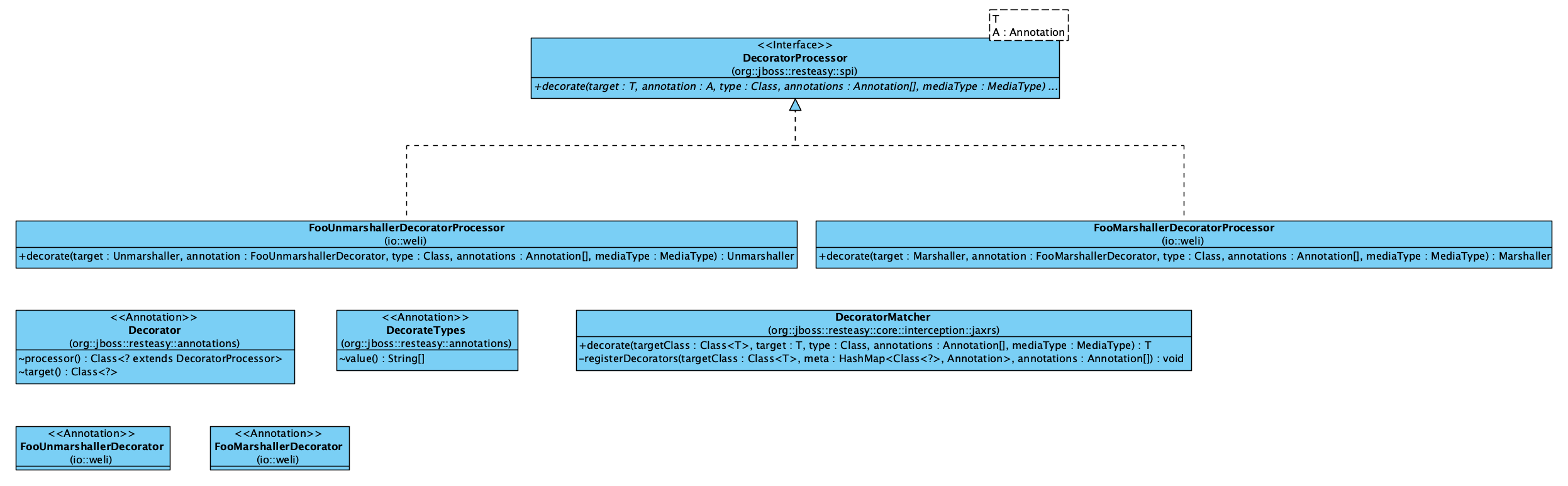
下面是这些classes的类图:
注意整个decorator机制是一个通用的独立设计,所以还需要在具体的provider里面使用起来才行。比如这里默认实现的AbstractJAXBProvider:
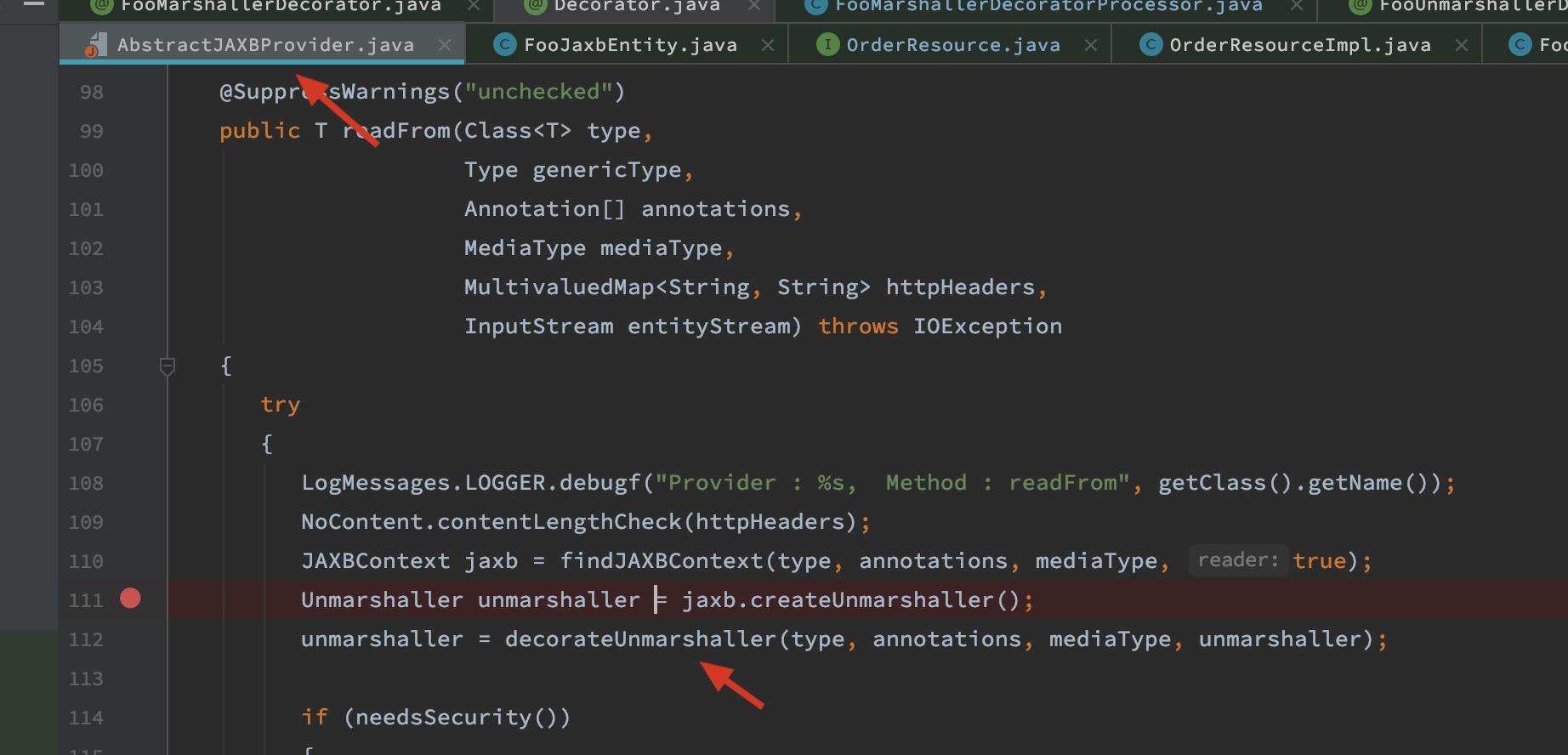
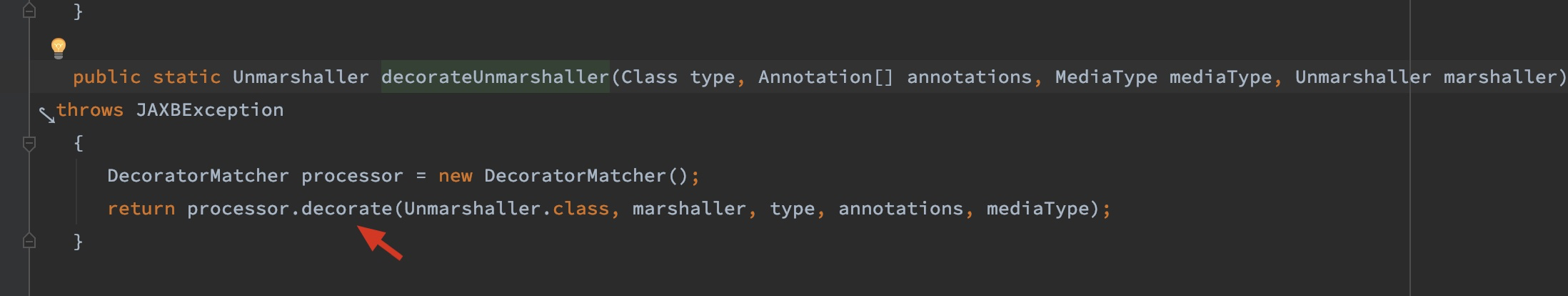
可以看到,decorator的具体使用入口是DecoratorMatcher,并且是和相关的provider具体实现搭配着来的。以上就是对decorator机制的分析。最后把测试相关的classes放出来:
本文中整个用到的代码放在了这里:
https://github.com/liweinan/Resteasy/commit/d442d1f1e80b581322213dac4a6f17b68d70fa50
有兴趣的可以看看。