The Analysis of AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor in Springframework
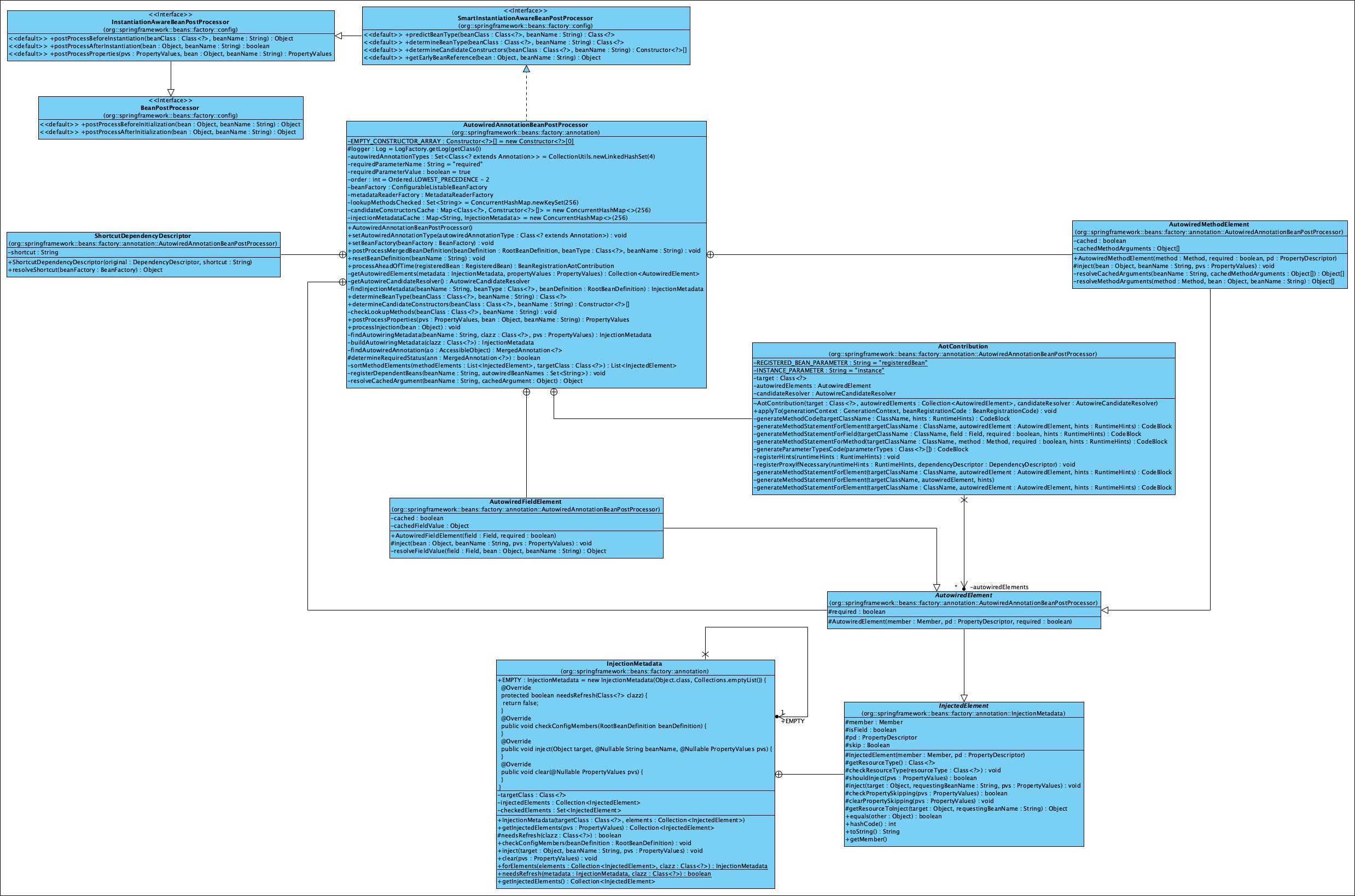
In Springframework, the AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor is used to deal with the @Autowired and the @Inject annotations and inject the beans. Here is the class diagram of AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor:
This is part of the javadoc of the class:
/**
* {@link org.springframework.beans.factory.config.BeanPostProcessor BeanPostProcessor}
* implementation that autowires annotated fields, setter methods, and arbitrary
* config methods. Such members to be injected are detected through annotations:
* by default, Spring's {@link Autowired @Autowired} and {@link Value @Value}
* annotations.
*
* <p>Also supports the common {@link jakarta.inject.Inject @Inject} annotation,
* if available, as a direct alternative to Spring's own {@code @Autowired}.
* Additionally, it retains support for the {@code javax.inject.Inject} variant
* dating back to the original JSR-330 specification (as known from Java EE 6-8).
...
It uses the autowiredAnnotationTypes internally to store the annotation types to process:
private final Set<Class<? extends Annotation>> autowiredAnnotationTypes = CollectionUtils.newLinkedHashSet(4);
/**
* Create a new {@code AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor} for Spring's
* standard {@link Autowired @Autowired} and {@link Value @Value} annotations.
* <p>Also supports the common {@link jakarta.inject.Inject @Inject} annotation,
* if available, as well as the original {@code javax.inject.Inject} variant.
*/
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor() {
this.autowiredAnnotationTypes.add(Autowired.class);
this.autowiredAnnotationTypes.add(Value.class);
ClassLoader classLoader = AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor.class.getClassLoader();
try {
this.autowiredAnnotationTypes.add((Class<? extends Annotation>)
ClassUtils.forName("jakarta.inject.Inject", classLoader));
logger.trace("'jakarta.inject.Inject' annotation found and supported for autowiring");
}
catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) {
// jakarta.inject API not available - simply skip.
}
try {
this.autowiredAnnotationTypes.add((Class<? extends Annotation>)
ClassUtils.forName("javax.inject.Inject", classLoader));
logger.trace("'javax.inject.Inject' annotation found and supported for autowiring");
}
catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) {
// javax.inject API not available - simply skip.
}
}
As the code shown above, it will process @Autowired, @Value and @Inject annotations by default. The usage is in the buildAutowiringMetadata() method:
private InjectionMetadata buildAutowiringMetadata(Class<?> clazz) {
if (!AnnotationUtils.isCandidateClass(clazz, this.autowiredAnnotationTypes)) {
return InjectionMetadata.EMPTY;
}
final List<InjectionMetadata.InjectedElement> elements = new ArrayList<>();
Class<?> targetClass = clazz;
do {
final List<InjectionMetadata.InjectedElement> fieldElements = new ArrayList<>();
ReflectionUtils.doWithLocalFields(targetClass, field -> {
MergedAnnotation<?> ann = findAutowiredAnnotation(field);
if (ann != null) {
if (Modifier.isStatic(field.getModifiers())) {
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info("Autowired annotation is not supported on static fields: " + field);
}
return;
}
boolean required = determineRequiredStatus(ann);
fieldElements.add(new AutowiredFieldElement(field, required));
}
});
final List<InjectionMetadata.InjectedElement> methodElements = new ArrayList<>();
ReflectionUtils.doWithLocalMethods(targetClass, method -> {
Method bridgedMethod = BridgeMethodResolver.findBridgedMethod(method);
if (!BridgeMethodResolver.isVisibilityBridgeMethodPair(method, bridgedMethod)) {
return;
}
MergedAnnotation<?> ann = findAutowiredAnnotation(bridgedMethod);
if (ann != null && method.equals(ClassUtils.getMostSpecificMethod(method, clazz))) {
if (Modifier.isStatic(method.getModifiers())) {
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info("Autowired annotation is not supported on static methods: " + method);
}
return;
}
if (method.getParameterCount() == 0) {
if (method.getDeclaringClass().isRecord()) {
// Annotations on the compact constructor arguments made available on accessors, ignoring.
return;
}
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info("Autowired annotation should only be used on methods with parameters: " +
method);
}
}
boolean required = determineRequiredStatus(ann);
PropertyDescriptor pd = BeanUtils.findPropertyForMethod(bridgedMethod, clazz);
methodElements.add(new AutowiredMethodElement(method, required, pd));
}
});
elements.addAll(0, sortMethodElements(methodElements, targetClass));
elements.addAll(0, fieldElements);
targetClass = targetClass.getSuperclass();
}
while (targetClass != null && targetClass != Object.class);
return InjectionMetadata.forElements(elements, clazz);
}
The above method uses the following method to find the expected annotations:
@Nullable
private MergedAnnotation<?> findAutowiredAnnotation(AccessibleObject ao) {
MergedAnnotations annotations = MergedAnnotations.from(ao);
for (Class<? extends Annotation> type : this.autowiredAnnotationTypes) {
MergedAnnotation<?> annotation = annotations.get(type);
if (annotation.isPresent()) {
return annotation;
}
}
return null;
}
The findAutowiringMetadata() method uses the buildAutowiringMetadata() method:
private InjectionMetadata findAutowiringMetadata(String beanName, Class<?> clazz, @Nullable PropertyValues pvs) {
// Fall back to class name as cache key, for backwards compatibility with custom callers.
String cacheKey = (StringUtils.hasLength(beanName) ? beanName : clazz.getName());
// Quick check on the concurrent map first, with minimal locking.
InjectionMetadata metadata = this.injectionMetadataCache.get(cacheKey);
if (InjectionMetadata.needsRefresh(metadata, clazz)) {
synchronized (this.injectionMetadataCache) {
metadata = this.injectionMetadataCache.get(cacheKey);
if (InjectionMetadata.needsRefresh(metadata, clazz)) {
if (metadata != null) {
metadata.clear(pvs);
}
metadata = buildAutowiringMetadata(clazz);
this.injectionMetadataCache.put(cacheKey, metadata);
}
}
}
return metadata;
}
The processInjection() method uses the above method:
/**
* <em>Native</em> processing method for direct calls with an arbitrary target
* instance, resolving all of its fields and methods which are annotated with
* one of the configured 'autowired' annotation types.
* @param bean the target instance to process
* @throws BeanCreationException if autowiring failed
* @see #setAutowiredAnnotationTypes(Set)
*/
public void processInjection(Object bean) throws BeanCreationException {
Class<?> clazz = bean.getClass();
InjectionMetadata metadata = findAutowiringMetadata(clazz.getName(), clazz, null);
try {
metadata.inject(bean, null, null);
}
catch (BeanCreationException ex) {
throw ex;
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(
"Injection of autowired dependencies failed for class [" + clazz + "]", ex);
}
}
In the above method, the metadata.inject() method will be used to process the bean injection. Here is the code of the InjectionMetadata.inject() method:
public void inject(Object target, @Nullable String beanName, @Nullable PropertyValues pvs) throws Throwable {
Collection<InjectedElement> checkedElements = this.checkedElements;
Collection<InjectedElement> elementsToIterate =
(checkedElements != null ? checkedElements : this.injectedElements);
if (!elementsToIterate.isEmpty()) {
for (InjectedElement element : elementsToIterate) {
element.inject(target, beanName, pvs);
}
}
}
The InjectedElement class is an inner class of InjectionMetadata, and the inject() method is like this:
/**
* Either this or {@link #getResourceToInject} needs to be overridden.
*/
protected void inject(Object target, @Nullable String requestingBeanName, @Nullable PropertyValues pvs)
throws Throwable {
if (!shouldInject(pvs)) {
return;
}
if (this.isField) {
Field field = (Field) this.member;
ReflectionUtils.makeAccessible(field);
field.set(target, getResourceToInject(target, requestingBeanName));
}
else {
try {
Method method = (Method) this.member;
ReflectionUtils.makeAccessible(method);
method.invoke(target, getResourceToInject(target, requestingBeanName));
}
catch (InvocationTargetException ex) {
throw ex.getTargetException();
}
}
}
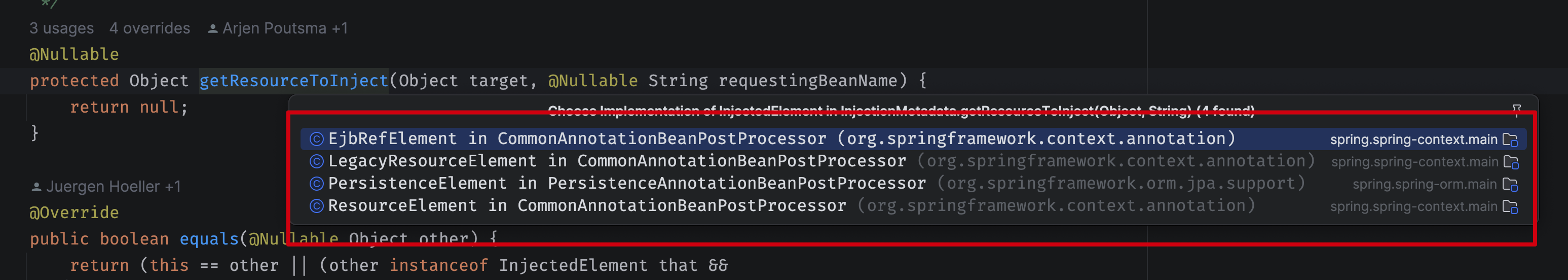
In the above code it set the field of the bean reflectively, and it uses the getResourceToInject() method generate the instance of the field to use. Here is the default implementation of the getResourceToInject() method:
@Nullable
protected Object getResourceToInject(Object target, @Nullable String requestingBeanName) {
return null;
}
Here are the implementations of the above methods:
One of the implementations is the ResourceElement in the CommonAnnotationBeanPostProcessor. I may write another blog post to analyse the detail of the processor.