Using Github Package together with Github Action
These two articles introduces how to use the Github Package Registry to deploy Maven artifacts and how to refer to the package in another project:
- How to use a private Maven repository in Artifactory with GitHub Actions
- Using GitHub Workflow with Maven dependencices from a private GitHub Package Registry
The above two articles are well written, so I won’t cover too many details in this blog post, and I’ll just write down some notes regarding with the usages.
Suppose there are two Github hosted Maven based projects called Foo and Bar:

As the diagram shown above the project Bar depends on project Foo. Suppose the project Foo has a stream version:
<?xml version="1.0"?>
<project xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 https://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd"
xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>io.my</groupId>
<artifactId>foo</artifactId>
<version>1.0.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
...
</project>
Which means the head version of project Foo will always be 1.0.0-SNAPSHOT. In project Bar the pom.xml contains a dependency item like this:
<dependency>
<groupId>io.my</groupId>
<artifactId>foo</artifactId>
<version>1.0.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
</dependency>
Which means the project Bar will always use the SNAP version of the project Foo. To make Foo be able to be referred by Bar, we need to deploy the Foo to Github Package. Because the above articles have introduces the details about this process, so I will just give some notes here and won’t go through the whole process. In general, in the pom.xml of project Foo, it needs to add the GitHub repository like this:
<distributionManagement>
<repository>
<id>github</id>
<name>Foo Package</name>
<url>https://maven.pkg.github.com/<your_account_name>/<your_project_name></url>
</repository>
</distributionManagement>
The above distributionManagement tells Maven the position that the project needs to be deployed to, then we can build and the project Foo:
$ mvn install
And then we can do the deployment with the following command:
$ mvn deploy
The above command will deploy the built package to Github Package. Taking one of my person projects for example:
In the pom.xml of the project it has the distributionManagement setting like this:
<distributionManagement>
<repository>
<id>github</id>
<name>weli's java-snippets package</name>
<url>https://maven.pkg.github.com/liweinan/java-snippets</url>
</repository>
</distributionManagement>
Here is the output of the mvn deploy command:
➤ mvn deploy
...
[INFO] --- maven-jar-plugin:2.4:jar (default-jar) @ java-snippets ---
[INFO] Building jar: /Users/weli/works/java-snippets/target/java-snippets-1.0-SNAPSHOT.jar
[INFO]
[INFO] --- maven-install-plugin:2.4:install (default-install) @ java-snippets ---
[INFO] Installing /Users/weli/works/java-snippets/target/java-snippets-1.0-SNAPSHOT.jar to /Users/weli/.m2/repository/io/weli/java-snippets/1.0-SNAPSHOT/java-snippets-1.0-SNAPSHOT.jar
[INFO] Installing /Users/weli/works/java-snippets/pom.xml to /Users/weli/.m2/repository/io/weli/java-snippets/1.0-SNAPSHOT/java-snippets-1.0-SNAPSHOT.pom
[INFO]
[INFO] --- maven-deploy-plugin:2.7:deploy (default-deploy) @ java-snippets ---
Downloading from github: https://maven.pkg.github.com/liweinan/java-snippets/io/weli/java-snippets/1.0-SNAPSHOT/maven-metadata.xml
Uploading to github: https://maven.pkg.github.com/liweinan/java-snippets/io/weli/java-snippets/1.0-SNAPSHOT/java-snippets-1.0-20230814.154741-1.jar
Uploaded to github: https://maven.pkg.github.com/liweinan/java-snippets/io/weli/java-snippets/1.0-SNAPSHOT/java-snippets-1.0-20230814.154741-1.jar (364 kB at 49 kB/s)
Uploading to github: https://maven.pkg.github.com/liweinan/java-snippets/io/weli/java-snippets/1.0-SNAPSHOT/java-snippets-1.0-20230814.154741-1.pom
Uploaded to github: https://maven.pkg.github.com/liweinan/java-snippets/io/weli/java-snippets/1.0-SNAPSHOT/java-snippets-1.0-20230814.154741-1.pom (8.0 kB at 1.5 kB/s)
Downloading from github: https://maven.pkg.github.com/liweinan/java-snippets/io/weli/java-snippets/maven-metadata.xml
Downloaded from github: https://maven.pkg.github.com/liweinan/java-snippets/io/weli/java-snippets/maven-metadata.xml (232 B at 75 B/s)
Uploading to github: https://maven.pkg.github.com/liweinan/java-snippets/io/weli/java-snippets/1.0-SNAPSHOT/maven-metadata.xml
Uploaded to github: https://maven.pkg.github.com/liweinan/java-snippets/io/weli/java-snippets/1.0-SNAPSHOT/maven-metadata.xml (764 B at 304 B/s)
Uploading to github: https://maven.pkg.github.com/liweinan/java-snippets/io/weli/java-snippets/maven-metadata.xml
Uploaded to github: https://maven.pkg.github.com/liweinan/java-snippets/io/weli/java-snippets/maven-metadata.xml (312 B at 101 B/s)
[INFO] ------------------------------------------------------------------------
[INFO] BUILD SUCCESS
[INFO] ------------------------------------------------------------------------
[INFO] Total time: 31.689 s
[INFO] Finished at: 2023-08-14T23:48:13+08:00
[INFO] ------------------------------------------------------------------------
weli@192:~/w/java-snippets|master⚡*
From the above output we can see the package is deployed to:
https://maven.pkg.github.com/liweinan/java-snippets/io/weli/java-snippets/1.0-SNAPSHOT/java-snippets-1.0-20230814.154741-1.jar
Please not there is timestamp automatically added at the end of the version number. This feature is important to avoid version conflict for each build and deployment. Here is the package page of the java-snippets:
And in the page you can see the different versions I’ve already deployed to Github Package. As we deployed the package by running the mvn deploy command locally after building the package locally. To automate this process, we can setup the Github Action like this:
I won’t go through the details, but here are some notes: Firstly the Maven setting need to be set in the action:
- name: Set up JDK 19
uses: actions/setup-java@v3
with:
java-version: '19'
distribution: 'temurin'
server-id: github # Value of the distributionManagement/repository/id field of the pom.xml
settings-path: $\{\{ github.workspace \}\} # location for the settings.xml file
And in the deployment step the auto-generated GITHUB_TOKEN needs to be set:
- name: Deploy
run: mvn -s $GITHUB_WORKSPACE/settings.xml deploy
env:
GITHUB_TOKEN: $\{\{ github.token \}\}
Note: I have to escape all the double parentheses in this blog post, or it won’t display.
Because I owned this repository, so this generated token can have the access to upload the package of this project. Now as the package is hosted in Github Package, we can start to use the package. Because this java-snippet project is public, so you just need to set the repository in the pom.xml of the project that want to refer to the package (Use Foo in Bar for example). Here is the setting example:
<repositories>
<repository>
<id>github</id>
<name>weli's java-snippets package</name>
<url>https://maven.pkg.github.com/liweinan/java-snippets</url>
</repository>
</repositories>
And then add the dependency:
<dependency>
<groupId>io.weli</groupId>
<artifactId>java-snippets</artifactId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
</dependency>
To sum up, here is the example:
To run this example, you can clone the repository into your local environment and run the Maven command:
$ mvn install
And in the above command output you can see something like this:
...
Downloading from github: https://maven.pkg.github.com/liweinan/java-snippets/io/weli/java-snippets/1.0-SNAPSHOT/java-snippets-1.0-20230814.163936-4.pom
Downloaded from github: https://maven.pkg.github.com/liweinan/java-snippets/io/weli/java-snippets/1.0-SNAPSHOT/java-snippets-1.0-20230814.163936-4.pom (8.0 kB at 3.2 kB/s)
...
So the java-snippets package can be downloaded from the Github Package.
The above setting is for the public project and package, if the package Foo is private, the situation goes complicated, because you need to set up the access token and use it properly. I won’t go into the details on how to generate the Github Repository Token with necessary privileges to access the private repository and the package, because the articles I referred in the beginning of this blog post already describes all the details. In general, you need to have a token that can have the access to read the package, and put it in your local Maven config file ~/.m2/settings.xml. Here is my settings in my local configuration file for example:
<servers>
<server>
<id>github</id>
<username>liweinan</username>
<password>my_token</password>
</server>
</servers>
In the above setting, liweinan is my Github account name and the password is the token I generated from Github that can access my private repository and package. Please note the id of the server needs to be conformed with the repositories and the distributionManagement id settings, or Maven can’t use the above setting accordingly.
If you want to automate the build process in Github Action, then you also need to setup the above security settings properly. The articles I referred to in the beginning of this blog post contains the detail on how to set it properly, and here are some notes:
First you need to put this setting in your maven.yml of your project Bar, which depends on Foo in building process:
- name: Set up JDK 17
uses: actions/setup-java@v3
with:
java-version: '17'
distribution: 'adopt'
server-id: github # Value of the distributionManagement/repository/id field of the pom.xml
settings-path: $\{\{ github.workspace \}\} # location for the settings.xml file
server-username: GITHUB_USER_REF # env variable name for username
server-password: GITHUB_TOKEN_REF # env variable name for GitHub Personal Access Token
And the above GITHUB_USER_REF and GITHUB_TOKEN_REF are Github Action environment variables:
env:
GITHUB_USER_REF: $\{\{ secrets.GH_PACKAGE_REPO_USERNAME \}\}
GITHUB_TOKEN_REF: $\{\{ secrets.GH_PACKAGE_REPO_PASSWORD \}\}
These are called Github Repository Secrets that you should define in your project’s Repository Secret section like this:
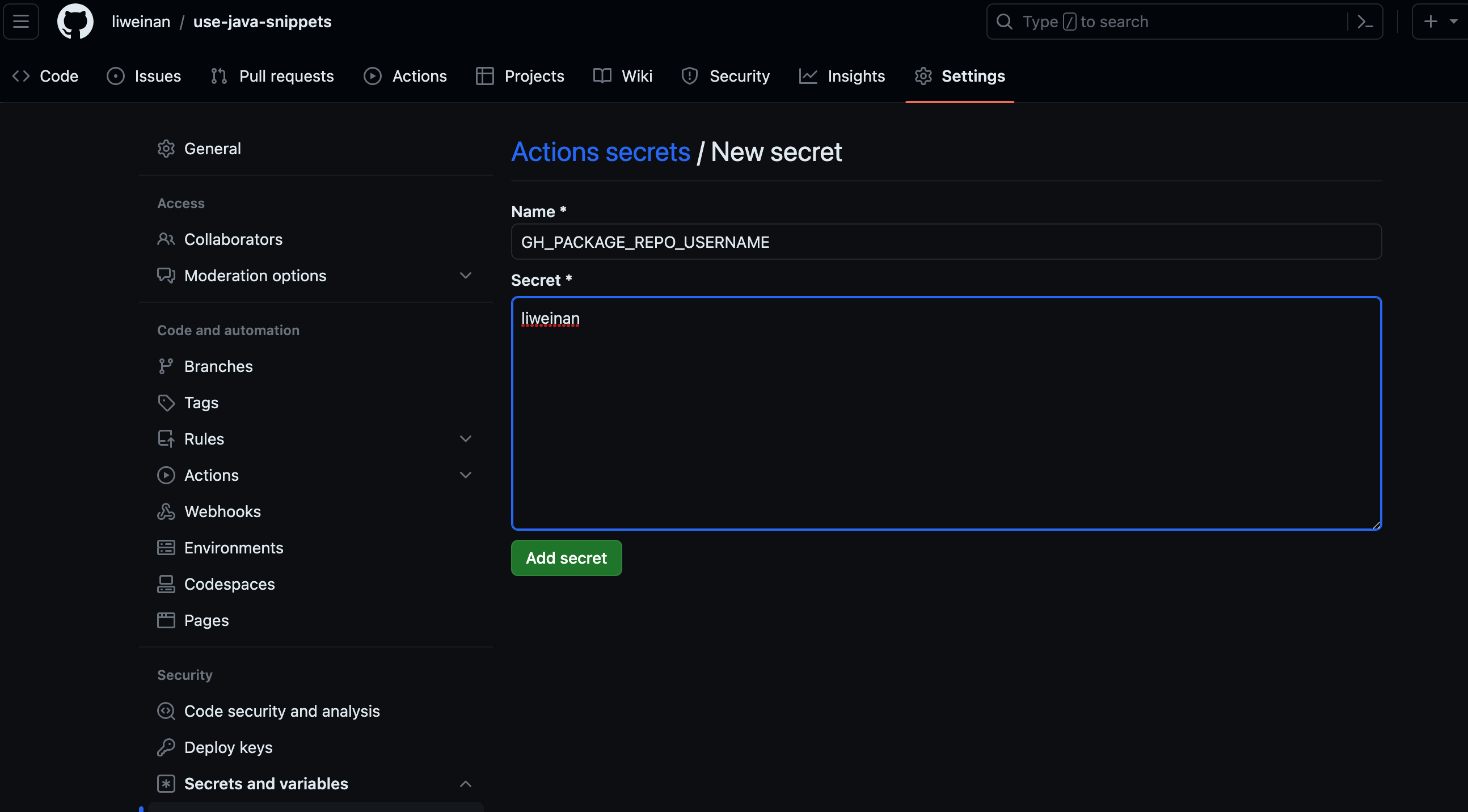
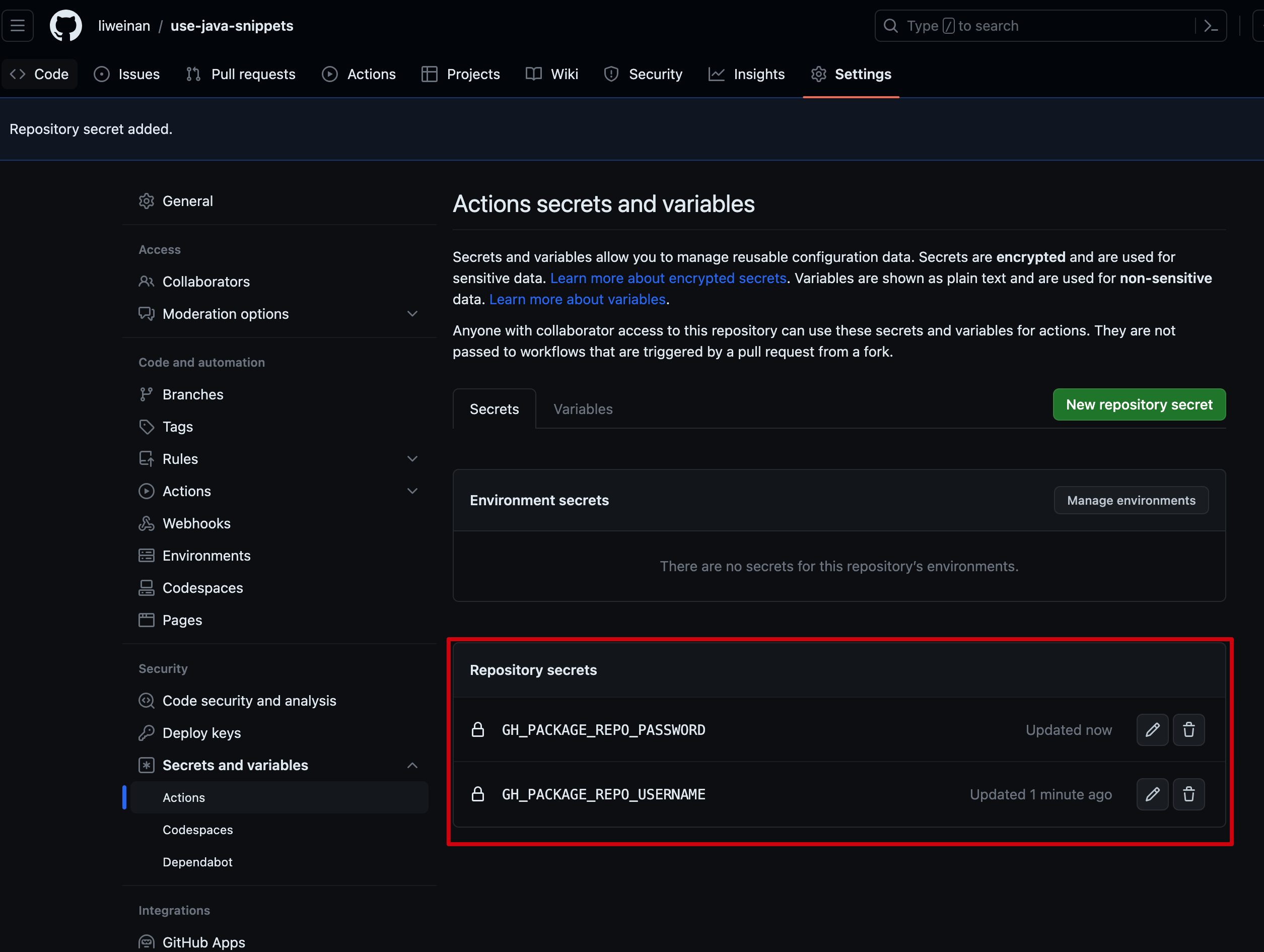
As the screenshots shown above, the GH_PACKAGE_REPO_USERNAME is my Github account name liweinan, which can have access to my personal private repo, and the GH_PACKAGE_REPO_PASSWORD is the token I generated that can have access to my private repo’s packages.
To sum up, here is an example Github Action setting that works:
Please note the java-snippets project in the example is a public project, so we don’t have to set up the token in Github Action, but for private repos and its packages, the above setting is a must-have.
Above is the notes I want to share with you on using the Github Package and Github Action, hope it’s useful to you :D